What Is a Pyranometer and Why You Need It for PV Projects
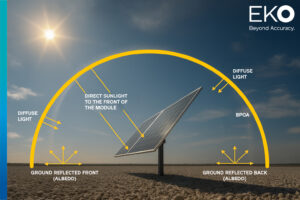
A pyranometer is a scientific sensor that measures solar irradiance — the total amount of energy reaching the Earth’s surface, expressed in W/m². It captures both direct sunlight and diffuse sky radiation, providing a precise measurement of the total solar energy available at a location.
Originally used in climate research and agriculture, pyranometers are now essential tools in photovoltaic (PV) projects. Their measurements are a critical input for calculating the Performance Ratio (PR) — a key metric that shows how efficiently a PV system converts sunlight into electricity.
How It Works
A pyranometer uses a detector covered by a glass dome that absorbs solar radiation and converts it into a small electrical signal proportional to sunlight intensity. This signal is then measured and recorded to quantify the solar energy.
Types of Pyranometers
- Thermopile Pyranometers: These are the most common type. They use temperature differences on a black surface to generate voltage and offer high accuracy across a wide spectral range. The MS-80SH is a top-tier Class A pyranometer ideal for precise solar assessments.
- Silicon Photocell Pyranometers: These use silicon detectors and are more affordable, suitable for general monitoring. However, they have a narrower spectral response and lower accuracy under variable weather conditions. Use the ML-01 silicon sensor for rapid-response applications.
Why You Need Solar Irradiance Data for PV Projects
Solar irradiance data is vital for successful planning, operation, and valuation of PV systems.
1. Accurate Solar Resource Assessment
Before construction, understanding the site’s solar resource is essential. Pyranometers measure global horizontal irradiance (GHI), which directly influences energy yield estimates. This data helps engineers:
- Design systems for optimal performance
- Predict energy production
- Secure project financing with credible solar data
2. Optimizing Operation and Performance Monitoring
During operation, pyranometers provide real-time irradiance data to compare expected vs. actual energy output. This enables:
- Calculation of Performance Ratio (PR)
- Early detection of issues like shading or equipment faults
- Timely maintenance to maximize uptime and revenue
3. Supporting Due Diligence and Asset Valuation
Accurate irradiance data builds trust during project transactions. Pyranometer data helps investors and buyers by:
- Providing transparent historical performance records
- Reducing investment risk
- Validating energy output against performance guarantees
4. Facilitating Advanced Analytics and Forecasting
Pyranometers also support grid integration and financial planning by enabling:
- Short-term energy generation forecasting
- Long-term performance modeling
- Improved revenue projections
Conclusion
A pyranometer is more than just a solar sensor — it’s a foundational tool for every stage of a PV project. From initial design and operational efficiency to valuation and forecasting, pyranometers reduce uncertainty and unlock greater project value.
